Guillain Barré Syndrome (GBS) is an uncommon and life-threatening illness that occurs when the immune system of the body starts to attack the peripheral nervous system. This syndrome has the potential to cause numbing, weakness, and in some cases, paralysis. In this blog post we will attempt to simplify GBS so it is easy to understand its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment and recovery. This guide can be used to clarify GBS for yourself or your close acquaintances in a manner that makes sense.
Table of Contents
What is the meaning of Guillain Barré Syndrome (GBS)?
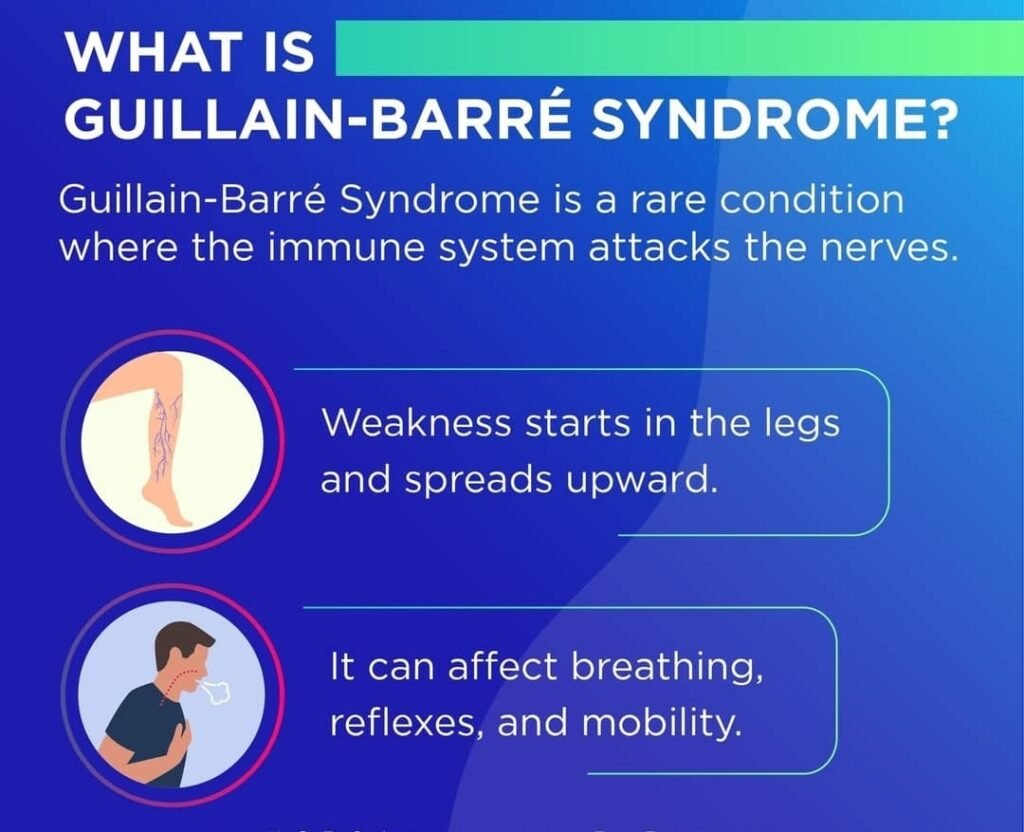
In its simplest terms, it is an autoimmune disorder that directly affects the nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. It usually starts as getting weak or a tingling sensation in the legs and at times can gets so severe that it results in the patient being fully paralyzed. Although it is not common, GBS is an ailment medical professionals need to attend to as fast as possible as it can result in danger to life.
Symptoms of Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) which are more common
One common feature of developing symptoms for GBS is that they tend to develop at a rapid pace and worsen between days or weeks. Here are some details about the most common signs to watch for:
• Tingling Sensations: Mostly starts from the toes, fingers, or legs.
• Muscle Weakness: Usually begins in the lower limbs and spreads upward.
• Difficulty Walking: Here, it becomes challenging to walk or even stand due to weak legs.
• Weakness of Facial Muscles: Facial expressions such as smiling, chewing, and closing of eyes is difficult.
• Pain: There is an aching or cramping pain especially at nights.
• Breathing Problems: In acute cases, the muscles responsible for breathing get affected.
• Abnormal heart rate or blood pressure: This occurs due to damage to autonomic nerves.

Causes and Risk Factors of Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
The precise reason behind Guillain Barré Syndrome is still a mystery. Although, infections often seem to trigger it. They are the main suspects.
• Bacterial Infections: Such as Campylobacter jejuni which is usually seen in foods that are contaminated.
• Viral Infections: Epstein – Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, Zika virus etc.
• Vaccination or Surgery: In rare cases, vaccines or surgeries tend to serve as triggers.
• Auto Immune Response: The immune system erroneously attacks healthy nerve tissues.
How do you diagnose Guillain Barré Syndrome (GBS)
Getting a diagnosis on GBS can be complicated because it’s closely related to other manys neurological disorders. Nevertheless, doctors carry out the following tests to confirm it.
• Neurological Check: Ensures control over muscle and reflexes.
• Nerve Conduction Tests: Used to evaluate how effectively nerves transmit signals.
• Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): Determines levels of protein in cerebrospinal fluids.
• Blood tests: Identify other conditions that may be mimicking related symptoms.
Treatment Methods for the Guillain Barré Syndrome (GBS)
GBS has no known cure but treatments can span across coping mechanisms and manage its symptoms. A few common treatments are:
1. Plasma Exchange Therapy: A form of blood purification, whereby harmful antibodies are extracted from blood plasma.
2. Intravenous Immunoglobulin IVIG: Specially made Abs that neutralize antagonistic Abs.
3. Physical Rehabilitation: Aid in the restoration of strength and limitations of movement.
4. Ventilation Support: Needed when the syndrome affects mechanisms needed for breathing.
5. Pain Management: Alleviation of pain neuropathy through the use of pain medication.
Prognosis and Recovery of Guillain Barré Syndrome (GBS)
People suffering from GBS typically heal, though the process takes several weeks, months, or even years. Here’s a rough guide on the prognosis:
• Mild Cases: Recovery normally occurs within weeks.
• Severe Cases: Weakness ranging from persistent to recurrent may increase recovery time to months.
• Relapse: Occasionally, some patients might go through a relapse.
• Support: Physical therapy along with rehabilitation forms the core of strengthening.
Coping with Guillain Barré Syndrome (GBS)
Treating GBS may be both mentally and physically draining. Here are some pointers for coping post-diagnosis:
• Follow-Up Care: Schedule regular visits with your neurologist.
• Support Groups: Get in touch with patients with similar struggles.
• Changing Lifestyle: Improve diet and exercise regularly to hasten the healing process.
• Mental Health: Seek therapy or counseling for symptoms of anxiety or depression.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) related to Guillain Barré Syndrome (GBS)
Q1. Is Guillain-Barré Syndrome transmissible?
No GBS is not transmissible. It is an autoimmune process often induced by infections.
Q2. Is it possible for Guillain-Barré Syndrom to reoccur?
In a small number of patients, GBS may recur, but this is very uncommon. It is a condition known as Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP).
Q3. What is the average survival rate for individuals with Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
With corrected treatment, the prognosis for most individuals is excellent. Some suffer severe and potentially fatal complications, but they can all be treated.
Q4. Are children too predisposed to GBS?
Yes, though rare, young children are at the risk of contracting GBS and need to be treated urgently.
Q5. What dietary restrictions should I comply with while suffering from Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
Avoid consumables contents associated with Campylobacter, such as undercooked chicken.
Conclusion
Guillain-Barré Syndrome is an infrequent occurrence but for those that suffer, it is a dire disease and can provoke permanent damage in every facet of life. Identification of the symptoms, treatment as well as therapy is the most important cornerstones of the rehabilitation process. Most patients suffering from GBS achieve improvement in leading a normal and a healthy life as treatment modalities have progressed over the years and medical practitioners have a better understanding of the illness.
Recovery is achievable for you or your loved one, even if GBS has affected you. Stay up to date by getting healthcare support and rehabilitation that will help you build up your strength. Most importantly remember, you are not going through this alone, there is support that is available.

